
Women taking birth pills have higher incidences of depression at the 5% significance level (the p-value equals. After the study, two-sample t-tests are performed for each variable and it is found that one null hypothesis is rejected. Two groups of women (one taking birth controls, the other not) are followed and 20 variables are recorded for each subject such as blood pressure, psychological and medical problems. We conclude that mi and mj differ (at a% significance level if > LSD, whereĪ hypothetical study of the effect of birth control pills is done. The test statistic is improved by using MSE rather than sp2. This method builds on the equal variances t-test of the difference between two means. Pairwise comparison: Are two population means different?Ĥ Fisher Least Significant Different (LSD) Method.Three statistical inference procedures, geared at doing this, are presented: Fisher’s least significant difference (LSD) method Bonferroni adjustment to Fisher’s LSD Tukey’s multiple comparison methodģ Example 15.1 Sample means: Does the quality strategy have a higher mean sales than the other two strategies? Do the quality and price strategies have a higher mean than the convenience strategy? Does the price strategy have a smaller mean sales than quality but a higher mean than convenience? For any doubt/query, comment below.1 Lecture 13 Multiple comparisons for one-way ANOVA (Chapter 15.7)Īnalysis of Variance Experimental Designs (Chapter 15.3)Ģ 15.7 Multiple Comparisons When the null hypothesis is rejected, it may be desirable to find which mean(s) is (are) different, and how they rank. The fundamental strategy of ANOVA is to systematically examine variability within groups being compared and also examine variability among the groups being compared. One-way ANOVA compares three or more than three categorical groups to establish whether there is a difference between them. Thus, we can say that the means of all three subjects is the same.

Step 2 -ĭf total = 2 + 6 = 8 Step 3 - On referring to the F-Distribution table ( link), using df 1 = 2Īnd df 2 = 6 at α = 0.05: we get, F table = 5.14 Step 4 - μ e = (2 + 4 + 2)/3 = (8/3) = 2.67
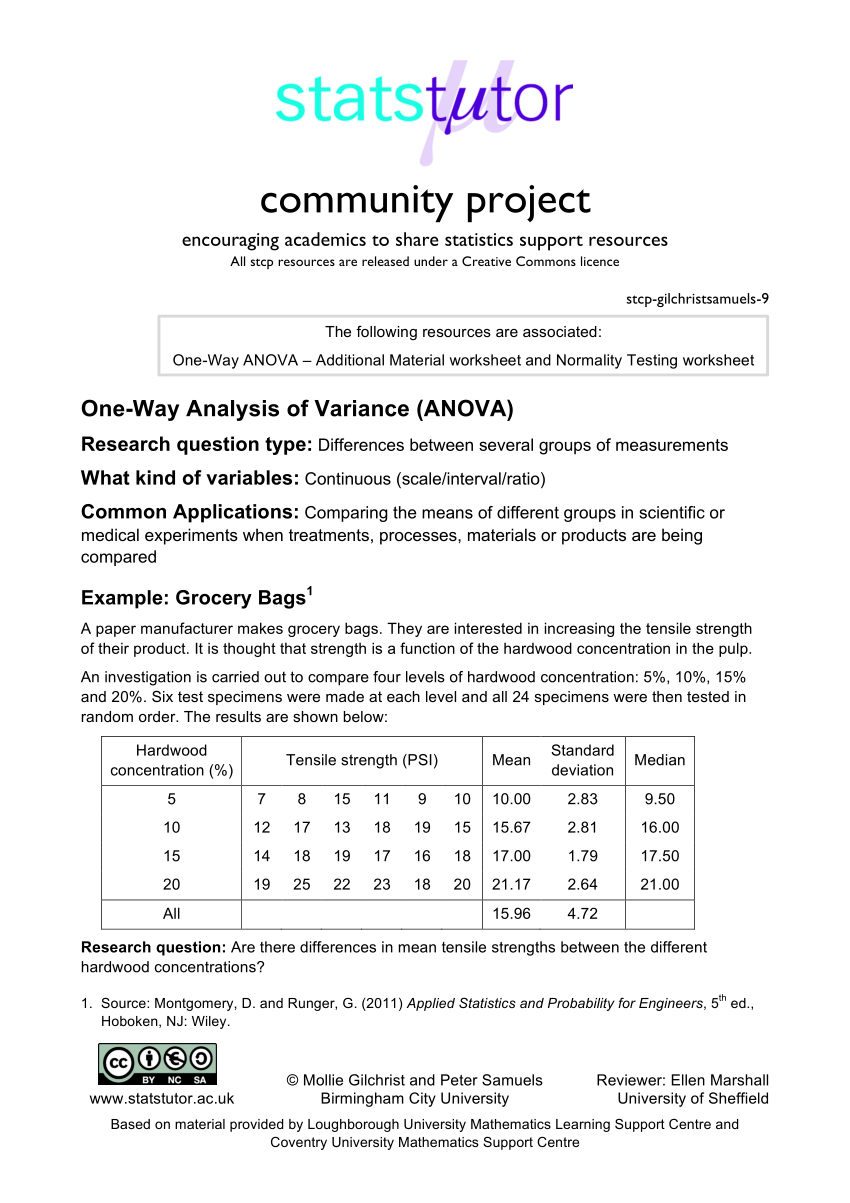
Null hypothesis, H 0 -> μ E = μ M = μ S (where μ = mean)Īlternate hypothesis, H a -> At least one difference among the means of the 3 subjects. Std/Sub English (e) Math (m) Science (s) Student 1 The marks of 3 subjects (out of 5) for a group of students is recorded.
#One way anova examples applied behavior analysis how to#
Interpreting the results if Fcalc Ftable :Ĭonsider the example given below to understand step by step how to perform this test. ML | Label Encoding of datasets in Python.ML | One Hot Encoding to treat Categorical data parameters.Introduction to Hill Climbing | Artificial Intelligence.Best Python libraries for Machine Learning.Activation functions in Neural Networks.Elbow Method for optimal value of k in KMeans.Decision Tree Introduction with example.Linear Regression (Python Implementation).



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
